light
light is that form of energy which gives us the sensation of vision . it is also the radiant form of energy . it is denoted by Q and it is expressed in lumen - hours and is analogues to watt-hours.
luminous flux
the light energy emitted in one second is called luminous flux . it is denoted by F and its expressed in lumen (LM).
luminous flux intensity
the luminous flux per unit solid angle is called luminous flux intensity . it is denoted by I.
I = F/W
its expressed in lumen/Sr or LM/Sr which is also called candela (Cd).
candle power
the total lumen per unite solid angle is called candle power . it is denoted by Cp
Cp=lumens/W
it is same as luminous intensity.
illumination
the luminous flux per unite area is called illumination .it is denoted by E.
illumination = luminous flux / area
E=F/A
It is expressed in Lm/M² which is also called LUX .
lamp efficiency
the lamp efficiency is define as the ratio of luminous flux to the input power .
lamp efficiency= luminous flux/input power
it is expressed in Lm/W
utilization factor[Uf]
the ratio of total lumens reaching to the working plane to the total lumens emitted by the lamp is called utilization factor or coefficient of utilization .
utilization factor =total lumens reaching to the working plane /total lumens emitted by lamp
maintenance factor
the ratio of illumination under normal working condition to the illumination under perfectly newly condition is called maintenance factor . and it is denoted by Mf
Mf=illumination under normal condition /illumination under newly condition
depreciation factor
the inverse of maintenance factor is called depreciation factor . it is denoted by Df.
Df=1/Mf
Frequency
the number of cycle completed in one second is called frequency .it is denoted by F and it is expressed in Hz.
frequency F=1/T where T = time required to completed one full cycle
time period
the time required to complete one full cycle is called time period . it is denoted by T and it is expressed in second .
Time period T =1/F where F = frequency
Amplitude
The maximum value of any A C quantity is called amplitude . the amplitude is also called peak value . the peak to peak value is defined as twice its maximum value .
Vpp=2Vm
RMS(root mean square) value
the RMS value define as that DC value which produce the heat when passing through given circuit for the given time as produce by AC current when passing through the same circuit for the same time .
Vrms=Vm/ √2 Irms=Im/ √2
Average value
the average value is define as that DC value which transfer the charge when passing through given circuit for the given time as transfer by AC current which passing through the same circuit for the same time .
Vav=2Vm/ 3.14 Iav=2Im/3.14
Active power
the power which is consumed in the circuit is called active power . active power also called real power and true power .it is expressed in watt(W) , kilowatt( KW) ,megawatt(MW) and it is denoted by P.
P=VICOSØ
reactive power
the power which is not consumed in the circuit is called reactive power . it is denoted by Q and it is expressed in VAR, KVAR ,MVAR.
Q=VI SINØ
apparent power
the product of the supply voltage and the total circuit current is called apparent power it is denoted by S and is is expressed in VA, KVA,MVA.
S=VI
S=√(P ²+Q ²)
Ohms law
the current flowing through conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it.
that is
V{ I
V=IR
where R is constant and is called resistance
that is
V/I=R
Kirchhoffs current law
the algebraic sum of current meeting at a junction is zero.
that is incoming current equal to the outgoing current .
I1+I2+(-I3)+(-I4)+I5+I6=0
I1+I2+I5+I6=I3+I4
Current divider formula
the formula which is used to find the branch current is called current divider formula.
the total circuit resistance is
Rt=(R1.R2/R1+R2)
The branch current is
I1=V/R1
I1=IRt/R1 (according to ohms law V=IR)
I1=(I/R1).(R1.R2/R1+R2)
I1=I.R2/R1+R2
similarly
I2=I.R1/R1+R2
Kirchhoffs voltage law (K V L)
The algebraic sum of EMF and voltage in any closed circuit is zero.
applying KVL to the circuit
-V1-V2+V=0
V=V1+V2
V=IR1+IR2
V=I(R1+R2)
Voltage divider formula (V D F)
The formula which is used to find the voltage across each resistor is called voltage divider formula.
total circuit resistance
Rt=R1+R2
The voltage across resistor R1
V1=IR1
V1=(V/Rt).R1 (according to ohms law I=V/R)
V1=(VR1/R1+R2)
similarly
V2=(VR2/R1+R2)
series connection of resistor
the circuit in which the voltage across resistor divides and current flowing through all resistor same is called series circuit . in this circuit all the resistors connected in series with each other. the below circuit diagram show series connection of resistor.
suppose a series circuit having three resistor of resistance R1,R2 and R3 let V1,V2 and V3 are the voltage across R1,R2 and R3 respectively and I is total current of circuit.
the total resistance is
Rt=R1+R2+R3
Voltage across resistor R1
V1=IR1
V1=(V/Rt).R1 (according ohms law V=IR therefore I =V/R) V1=(VR1/R1+R2+R3)
similarly
V2=(VR2/R1+R2+R3)
V3 =(VR3/R1+R2+R3)
parallel connection of resistor
the circuit in which main line current divides and voltage across all resistor same is parallel circuit . in this all resistor connected in parallel. the below circuit diagram show parallel connection of resistors.
suppose a parallel circuit having resistance R1,R2 and R3 let I1,I2 and I3 are the current through R1,R2 and R3 respectively
the total circuit current is
It=I1+I2+I3
V/Rt=(V/R1+V/R2+V/R3)
V/Rt=V(1/R1+1/R2+1/R3)
1/Rt=(1/R1+1/R2+1/R3)
Rt=(R1.R2.R3/R1+R2+R3)
A)Resonance in RLC series circuit(series resonance)
the condition at which the inductive reactance XL equal to the capacitive reactance Xc is called series resonance.the frequency at which this condition occur is called resonance frequency .it is denoted by Fr 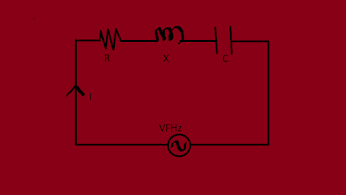

at resonance condition
XL=Xc
4
π²
F²rLC=1Fr²=1/4
π²
LCThis is required expression for resonance frequency.
the following are the effects of series resonance.
1)power factor is unity.
2)the current in the circuit is maximum.
3)inductive reactance equal to capacitive reactance







0 Comments