Conductor
the substance which is conduct electric current easily are called conductor . conductor have nearly to zero resistance . the copper , iron and aluminium are the example of the conductor .
on the basis of valence electron the conductor are these element which have less than four valence electron are called conductor on the basis of energy band diagram the element whose conduction band and valence band over lap with each other are called conductor
semi conductor
the substance which conductivity line between the conductor and insulator is know as semi conductor . carbon , silicon, germanium are the example of semi conductor.
on the basis of valence the semi conductor element which have four electron outermost shell called semiconductor on the basis of energy band diagram the semi conductor are these conduction band and valence band are separated by one electron forbidden band is called semiconductor
insulator
the substance which have zero conductivity (infinite resistance ) are called insulator . plastic .dry woodand rubber are the example of insulator on the basis of valence electron the insulator are those element which have more than four electron in its outermost orbit . on the basis of energy band diagram insulator are those element which conduction band and valence band are separated by large forbidden band .
valence band
the range of energy possess by the electron in the valence band are called valence band. in other word the valence bands a energy is called valance band .
conduction band
the range of energy passes by possess by the free electron are called conduction band . in other word the energy of free electrons is called conduction band .
forbidden band
the separation between conduction band and valence band is called forbidden band
Energy band diagram
the graphical representation of conduction band , valence band and forbidden band is called energy band diagram.
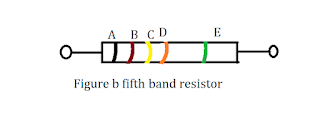
resistor colour coding
it is defined as the determination resistor value without using instrument just by inspection is called colour codes.
in this process the different band as show in figure' a'
and figure ' b' then the resistor value are calculated by
The following source band value of different colour
DIODE(CONSTRUCTION AND CHARACTERISTICS CURVE)
Diode is a semiconductor two terminal , solid state device , having positive and negative terminal .This semiconductor p- type and n-type form semiconductor diode the some time called semiconductor diode or p-n diode .figure shown the symbol of diode the arrow head represent the positive ( anode) and the bar represent the cathode .
The diode which is used in power electronic circuit is called power diode . The power diode is also define as the diode having high rating and mainly used for high power circuit . The construction that is layer structure symbol of the diode is shown .
When the positive terminal of the supply is connected to the anode and negative terminal of the supply is connected to the cathode. then the this mode of the diode is forward biased and voltage conduct . the diode conductor only when its applied voltage to the diode is greater than barrier potential . when the positive terminal of the supply connected to the cathode that is n-type material and negative terminal of supply is connected to the anode that is p-type , then this mode is called reverse biased and when the diode is revers biased then the small amount of current flows through the diode which is less than the current is forward mode . the V-I characteristics of diode is also clearly shown.
The following are the type of power diodes
1) General purpose power diode
the power diode whose current rating is 1A to 200A and voltage rating is 50 volt to 5KV is called general purpose diode .This type of power diode is mainly used for low frequency circuit .
2) fast recovery diode
the power diode whose current rating is 1A to few hundred amper and voltage rating is 50 volt to 3KV is called fast recovery diode .This type of power diode is mainly used in power electronic circuit .
3) schottky diode
the power diode whose current rating is 1A to 300A and voltage rating is up to 100 volt is called schottky diode .This type of power diode is mainly used for low voltage and high current dc power supply .
DIODE APPLICATION
Diode is used to convert AC in to pulsating DC .the circuit which convert AC into pulsating DC is called rectifier . the rectifier is two type such as
1) full wave rectifier
2) half wave rectifier
full wave rectifier
the rectifier which convert both the half cycle of AC input into pulsating DC is called a full wave rectifier .
figure shows a bridges full wave rectifier the bridges full wave used diode in a wheat stone bridges such that two diode are forward bias in each half cycle . during the positive half cycle of the AC input diode D1 and D3 are forward bias while the diode D2 and D4 are reverse bias hence current following through diode D1 and D3 in a closed loop ACDEFGBA .
During the negative half cycle of the AC input diode D1 and D3 are reverse bias while the diode D2 and D4 are forward bias hence current following through diode D2 and D4 in a closed BGDEFCAB . Fig shows the output wave form a positive half cycle , negative half cycle and complete cycle
half wave rectifier
the rectifier which convert only one half cycle of the AC input into pulsating DC is called half wave rectifier.
above figure show the rectification process by half wave rectifier .In this above figure during the positive cycle of the AC input the secondary winding of the transformer will have terminal A more positive with respect to terminal B hence the diode is forward bias hence current flow through load .
during the negative half cycle of the AC input the secondary winding of transformer will have terminal B more positive with respect to terminal A and diode D will be reverse biased hence there will no current conduct hence an negative half cycle the circuit is open . the output wave formed of half wave rectifier is shown in the figure.
basic electronic mcq
1)a ideal power diode must be have
a) low forward current carrying capacity
b) large reverse breakdown voltage
c) high ohmic junction resistance
d) high reverse recovery time
ANS: large reverse breakdown voltage
2) the V-I characteristic of the diode lie in the
a) 1st and 2nd quadrant
b) 1st and 4th quadrant
c) 1st and 3rd quadrant
d) only 1st quadrant
ANS: 1st and 3rd quadrant
3) a diode is said to be reversed biased when the
a) both cathode and anode are negative
b) cathode is negative and anode is positive
c) cathode is positive and anode is negative
d) none of these
ANS: cathode is positive and anode is negative
4) when the p-n junction diode is reverse biased , the width of the depletion region
a) increase the barrier potential
b) increase the width of the depletion layer
c) decrease the width of the depletion layer
d) none of these
ANS : decrease the width of the depletion layer
5) a power transistor is a
a) three junction and three layer device
b) two junction and three layer device
c) three junction and four layer device
d) one junction and two layer device
ANS :two junction and three layer device
6)which of the following device does not belong to the transistor family.
a) MOSFET
b) BJT
c) IGBT
d) GTO
ANS: GTO
7) in a BJT . the forward current gain alfa is given by
a) Ic/Ib
b) Ic/Ie
c) Ie/Ic
d) Ie/Ic
ANS: Ic/Ie
8) in a BJT . the forward current gain bitaa is given by
a) Ic/Ib
b) Ic/Ie
c) Ie/Ic
d) Ie/Ic
ANS: Ic/Ib
9) for a power transistor , which of the following relation is true
a) Ic>Ie>Ib
b) Ie>Ic>Ib
c) Ib>Ic>Ie
d) Ie=Ib
ANS: Ie>Ic>Ib
10) a thyristor (SCR) is a
a) PNP device
b) NPN device
c) PN device
d) PNPN device
ANS: PNPN device
11) a SCR is a
a) four layer and four junction device
b) four layer and three junction device
c) four layer and two junction device
d) three layer and single junction
ANS :four layer and three junction device
12) chose the correct statement
a) MOSFET is a uncontrolled device
b) MOSFET is a voltage controlled device
c) MOSFET is a current controlled device
d) MOSFET is a temperature controlled device
ANS: MOSFET is a voltage controlled device
13) which terminal does not belong to the SCR.
a) anode
b) base
c) gate
d) cathode
ANS: base
14) AN L filter is connected in
a) series
b) parallel
c) both a and b
d) none of the above
ANS: series
15) ac voltage controllers are used in ------------- application .
a) power generator
b) power transmission
c) conveyor belt motion
d) electric heating
ANS: electric heating
16) a TRIAC can be turn on with
a) positive voltage at the gate terminal
b) negative voltage at the gate terminal
c) either a or b
d) none of these
ANS: either a or b
17) in case of an L filter , the ripple current increases with
a) increase in load
b) decrease in load
c) increase in the value of L
d) ripple current never increases
ANS: decrease in load









0 Comments